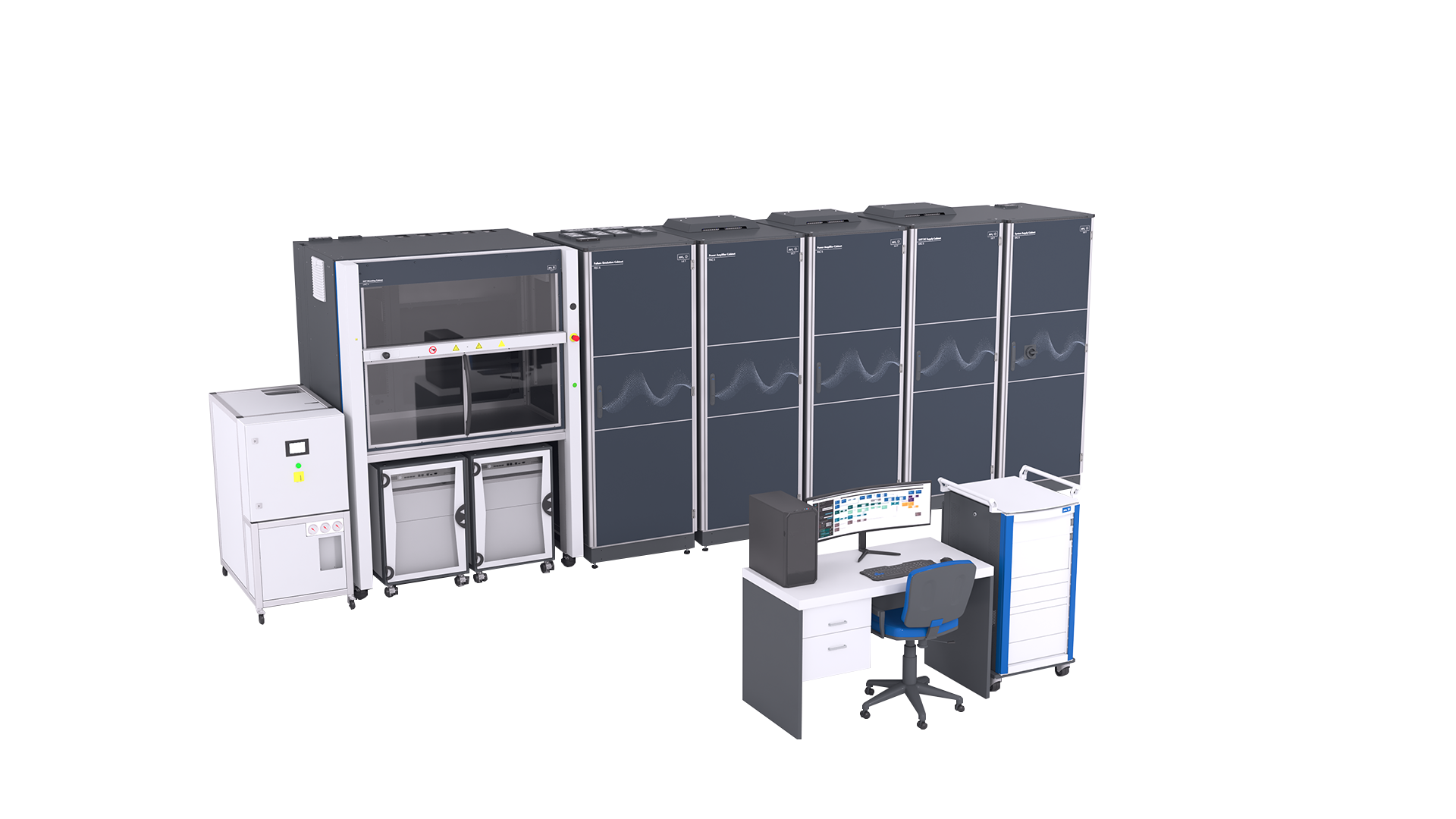
Application
Automotive
Automotive
Real solutions.
That simply has to be included.
We have been at the forefront of the automotive sector for over 10 years. Thanks to our clients who are the most demanding automotive players on the global market.
We concentrate on exactly what your testing, and hence your product, needs.

Automotive Requirements
We have found testing solutions for the special requirements in the automotive sector. Because power electronic components (such as drive inverters) are subject to a particular set of requirements.
These generally include:
High degree of efficiency
The efficiency of a drive inverter directly influences the range of an electric vehicle and the battery size. The efficiency of inverters tends to lie in the range 90-99% and depends heavily on the operating point. This is why the efficiency must be determined over a representative driving cycle (such as the WLTP) in order to be comparable.
Low volume and low performance weight
Mounting space in a vehicle is normally very limited and every component contributes to the weight of the vehicle. Normally, this weight has to be kept to a minimum to ensure the lowest possible losses in energy consumption.

High requirements for safety and reliability
The drive inverter is always safety-critical since it provides the torque on the wheel or a vehicle transmission via the e-motor. Any torque occurring that was not initiated by the driver could have fatal consequences. Vehicles with a torque-vectoring function normally even have an ASIL-D requirement.
High environmental requirements
In-vehicle devices are subject to increasingly strict requirements for maximum temperature, cycle stability, vibration resistance, humidity loading and other environmental influences.
High short-term load capacity
The acceleration and deceleration of a vehicle generates many times the steady state power flow in the drive inverter, whereby in both cases the events are transient and do not represent permanent conditions.
Low unit price
As for every vehicle component, the drive inverter is subject to a high level of cost pressure that requires consideration, on the one hand, during the development phase by selecting cost-favourable designs and components, and on the other, during the production process and during series testing.

High fault tolerance
Any faults occurring on the phase outputs of the drive inverter, such as short circuits between the phases, to the battery or to the chassis, or power interruptions, should not cause the device to fail and must be correctly recognised by the device.
Long lifetime
Vehicle inverter lifetime is at least 10 years. Although the inverter is not a wear part, the components in an inverter such as the intermediate circuit capacitor and power semiconductors do display fatigue effects over operational time. These effects must be minimized through optimal design and favourable operation.
Specific special functions
Since the e-motor does not have its own evaluation electronics, the drive inverter monitors the e-motor and prevents it from overloading. In addition, there are a number of special functions such as traction control and ABS.
Overload protection and diagnostic capability
The drive inverter must protect itself from overload (thermal, overcurrent, overvoltage) and be able to self-diagnose any hardware faults that may occur.